Login by Manually Specifying an Access Token
In this method, your application retrieves the access token from the SDK and stores it in the application storage. The application can later login with this token when the process is rebooted.
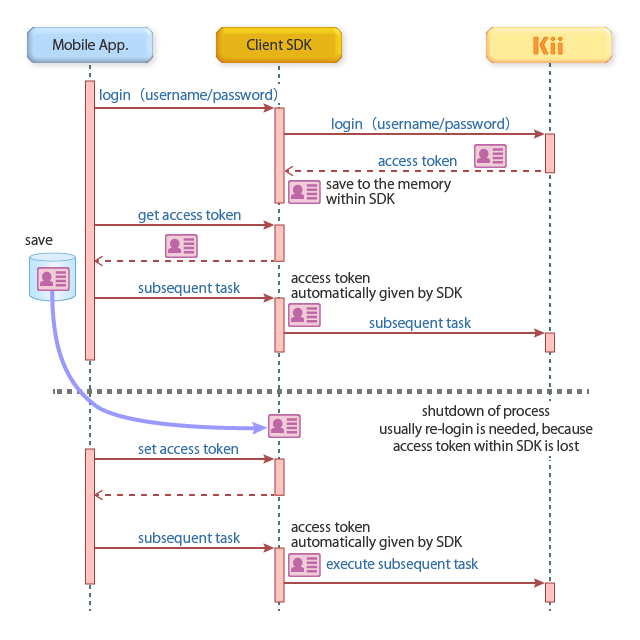
The access token for a user can be retrieved in two ways. One way is by calling the accessToken method. Another way is to get a dictionary by executing the accessTokenDictionary method and get token value from the dictionary with the access_token key. In both cases, you have to call the method while the user is logged in. The following sample code shows the both ways:
Swift:
// Assume that a user has logged in.
// Method #1: Get an access token from the accessToken property.
let token1 = KiiUser.current()!.accessToken
// Method #2: Get an access token with the accessTokenDictionary() method.
let dictionary = KiiUser.current()!.accessTokenDictionary()!
let token2 = dictionary["access_token"] as! NSString
// Securely store the access token in the storage with your own function.
storeToken(token)
Objective-C:
// Assume that a user has logged in.
// Method #1: Get an access token from the accessToken property.
NSString *token = [[KiiUser currentUser] accessToken];
// Method #2: Get an access token with the accessTokenDictionary method.
NSDictionary *dictionary = [[KiiUser currentUser] accessTokenDictionary];
token = [dictionary objectForKey:@"access_token"];
// Securely store the access token in the storage with your own function.
[self storeToken:token];
Here is the sample code for authenticating a user with an access token. By calling the authenticateWithToken:andBlock method with the access token, your user will be authenticated again.
Swift:
-
// Get an access token from the storage with your own function. let token = getStoredToken() do{ // Authenticate a user with the access token. try KiiUser.authenticate(withTokenSynchronous: token) }catch let error as NSError { // Handle the error. return } -
// Get an access token from the storage with your own function. let token = getStoredToken() // Authenticate a user with the access token. KiiUser.authenticate(withToken: token, andBlock:{(usr , error )->Void in if (error != nil) { // Handle the error. return } })
Objective-C:
-
NSError *error; // Get an access token from the storage with your own function. NSString *token = [self getStoredToken]; // Authenticate a user with the access token. [KiiUser authenticateWithTokenSynchronous:token andError:&error]; if (error != nil) { // Handle the error. return; } -
// Get an access token from the storage with your own function. NSString *token = [self getStoredToken]; // Authenticate a user with the access token. [KiiUser authenticateWithToken:token andBlock:^(KiiUser *user, NSError *error) { if (error != nil) { // Handle the error. return; } }];
Please make sure to store an access token in a secure place. It should not be accessible by other applications. If a malicious application gets the access token, it will gain privileges to access Kii Cloud as the owner of this token.
In this approach, your mobile app controls the access token. This allows your mobile app to manage multiple user logins by keeping the access tokens for them and by switching to the appropriate access token. The client SDK can only hold one access token at a time, so the mobile app needs to switch users).
Note that you cannot use the refresh token if you manually specify an access token for login. This is because this login method only restores the access token. In order to user the refresh token, you need to use the login method described in Login with the Auto-Saved Credentials.