Logging in and Using an Access Token
Kii Cloud identifies a logged-in user with their access token. To manage user login state, you need to understand how the access token works.
Access token
A user will get their access token from Kii Cloud when they sign up or sign in. The access token is s string for identifying authenticated users.
The client SDK will automatically store the access token in memory. The SDK will then send the access token to Kii Cloud when it sends subsequent requests to Kii Cloud. Handling the access token is automatically performed by the SDK, so your mobile app does not need to care about the access token in subsequent processes after the login (your mobile app just needs to be aware of whether a user is currently logged in or not).
If you are using the REST API, your mobile app needs to specify the access token explicitly in the Authorization header in the HTTPS request. Your mobile app also needs to preserve the access token obtained upon the login.
The following figure illustrates how the access token is used when a request is sent from the Kii Cloud SDK. If you use the REST API, you will implement functions that are equivalent to the Kii Cloud SDK in your own request module.
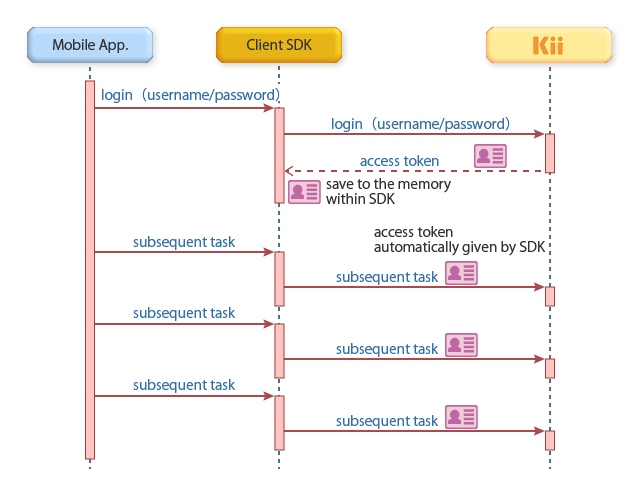
By providing an access token, any user can gain the same privilege on Kii Cloud data as when the token holder signs in with their username and password. It is therefore important to store the access token securely like the password.
The access token in the following two cases is handled differently.
When using Kii Cloud SDK for Thing, the thing will log in to Kii Cloud with the dedicated API and get the access token. See Thing Management for more details.
When using a pseudo user, your application needs to save the access token assigned to the user. See Pseudo Users for more details.
Keeping the user logged in
Since an access token is stored in a memory, it will be lost when the application is rebooted.
To restore the login state after reboot, use one of the following methods.
- Authenticate the user again by having the user re-enter the username and password, and get a new access token.
- Get and save an access token at user login, and use the saved access token to have the user log in.
- Use information including an access token that are automatically saved by the Kii Cloud SDK, and have the user log in. This method is available with the Kii Cloud SDKs for Android and iOS.
- If you use the REST API, save an access token on the client program.
By logging in with a Kii-provided access token, users will be free from typing in their username and password for each session. You can, for example, implement the "Keep Me Logged In" user interface.
An access token is invalidated when the user changes their password. In this case, the user needs to get a new access token by logging in with his username and password.
An access token is invalidated also when the user is disabled.
Token interoperability
Access tokens obtained via client SDKs and REST API are interoperable.
For example, you can get an access token via Kii Cloud SDK for Android and then uses the same token for executing REST API.
Managing the app state
With Android, you can save the internal session information at the following two levels for the restart of activities and processes.
For the restart of activities
Implement the
onSaveInstanceState()method and theonCreate()method for the restart of activities as described in Tips for Implementing with Android.Call the
Activity.onSaveInstanceState()method just before the activity is destroyed so as to store the internal information in a bundle. After the activity is restarted, call theKii.onRestoreInstanceState()method and restore the internal information from the bundle.Note that this method does not restore the internal information when a process is restarted.
For the restart of processes
Save an access token to the shared preferences for the restart of processes as described in Login by Manually Specifying an Access Token or Login with the Auto-Saved Credentials.
You can keep the login state after the mobile app exits by using this method.